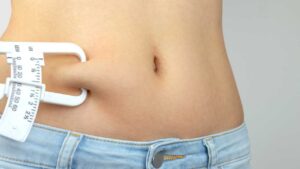
Top 7 Benefits of Mounjaro for Weight Loss
If you’re tired of trying every diet and exercise plan without seeing lasting results, Mounjaro might be exactly what you need. This medication is making waves in the weight loss world, and for good reason. It not only helps you lose weight but also gives your body the support it